Background Agricultural Connections
Plants provide perfect living specimens for comparing sexual reproduction (AKA propagation) and asexual reproduction. Focusing on plants that provide edible products (fruits, vegetables, flowers, etc.) can assist in engaging students and peaking their interest – it seems that everyone can relate to FOOD!
Many times seeds are thought of as lifeless objects without “vital signs.” However, each seed contains genetic information from a male and female parent. This information is contained in the small (sometimes microscopic) embryo inside of the seed. The development of a seed can be attributed to the flower, pollination and fertilization processes (see attached student reading Seed to Seed 101). Corn is a common agricultural plant grown in Minnesota, and many other regions of the United States, that can be used to demonstrate the seed production process. The steps are described below.
- Corn seeds (or kernels) are planted in the soil.
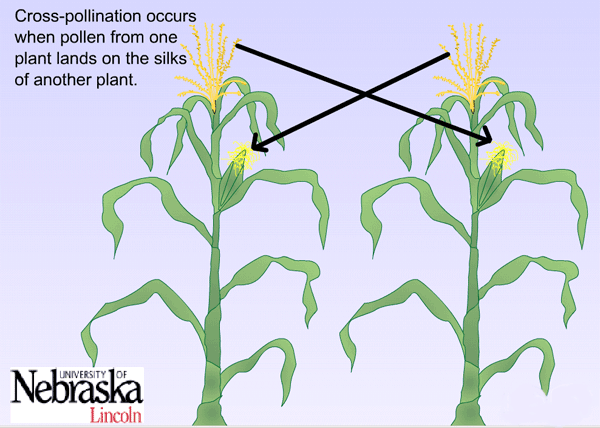
- With proper nutrients, light and water, this kernel develops into a plant that contains both male and female parts of a plant. The male part is called the tassel and is found at the top of the corn plant. The female parts of the corn plant, called silks, are found in the shoot that will develop into the ear of corn – the ear shoot.
- The tassel holds pollen. This pollen is transferred to the female ear shoot that contains 750-1000 ovules that each produces a silk. If a pollen grain reaches a silk then a kernel will develop. Each kernel that develops on an ear of corn is a separate individual with different genetics. However, the kernels on an ear of dent corn will all look very similar because plant geneticists and crop scientists have done years of plant breeding and selection to limit the trait variation. Farmers want to produce the corn with the highest yields (production) and also plants that can survive droughts, resist insects and disease, and have the same number of days to maturity. For these reasons, there is limited variation in the offspring (kernels) produced.
Students will research the flowers of vegetable and fruit plants and illustrate how the genetics from the parent plants produce a new seed, which will develop into a new plant.
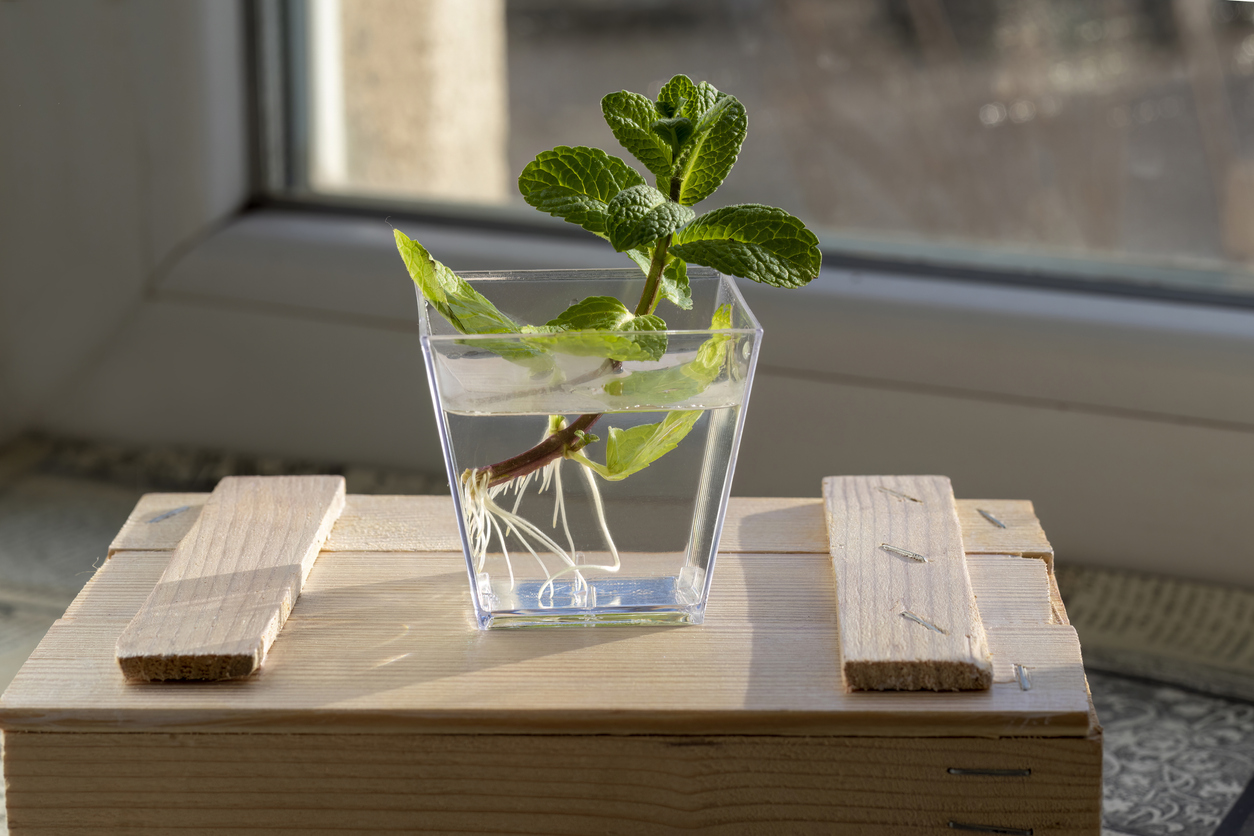
Plants also have the ability to reproduce without utilizing the genes from parents. This process of reproduction is called asexual reproduction. Plant scientists routinely refer to asexually reproduction as vegetative propagation. In asexually propagation, a complete plant can be regenerated from a severed piece of stem, root, a bud, leaf or even a small group of certain plant cells. The new plant that is generated will be genetically identical to the plant that it was “cut” from. The phenomenon of asexually propagation can be easily demonstrated in a classroom using stem cuttings. Students cut off a small portion of the stem of a plant (see Stock Plant lists for examples). This “wounds” the plant and cuts off the water supply. When this cutting (removed portion of the plant) is placed in soil or water and provided with light – new roots will be developed and a new plant will be on its way! Roots are most likely to develop at a stem wound that is in firm contact with moist soil. When a plant is wounded, hormones called auxins collect briefly around the wound and cause cell division so that it begins to form embryonic root tissue. This tissue develops into fully functioning roots and the plant will continue to grow leaves, stems and additional plant parts identical in genetic make-up to the parent plant.
The processes of planting seeds and also taking stem cuttings are easy and fun activities for students to complete. The plants that result are perfect for inquiries, discussions, and experiments on genetics and the environment.

